News
ACS Nano highlights latest work on graphene
One of the latest group publications " Redox-Dependent Spatially Resolved Electrochemistry at Graphene and Graphite Step Edges" published in ACS Nano earlier this month has been highlighted as one of the top 10 articles in this month's "In Nano" review. Congratulations to all involved!
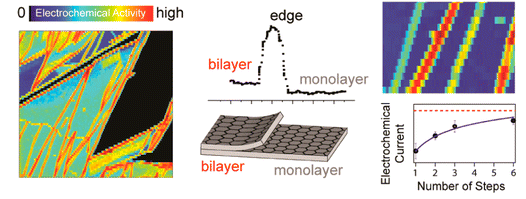
The work by the team studies the basal surfaces and step edges of graphene and highly oriented pyrolytic graphite (HOPG) using Ru(NH3)6 3+/2+, a redox probe whose standard potential lies near the intrinsic Fermi level of graphene and graphite. Using scanning electrochemical cell microscopy and other complementary microscopy techniques, including atomic force microscopy and micro-Raman, the group found a strong dependence of the electron transfer kinetics on the number of graphene layers, with rates increasing with layer number. In graphene and HOPG that were analysed at similar time points after cleavage, there were distinct differences in the electrochemical activity between basal planes and step edges. These differences were accentuated over time in HOPG. The authors suggest that these findings could lead to better understanding of both materials, which could eventually advance their use in a variety of applications.
